The results of the search for protein-protein interactions is summarized using several tables:
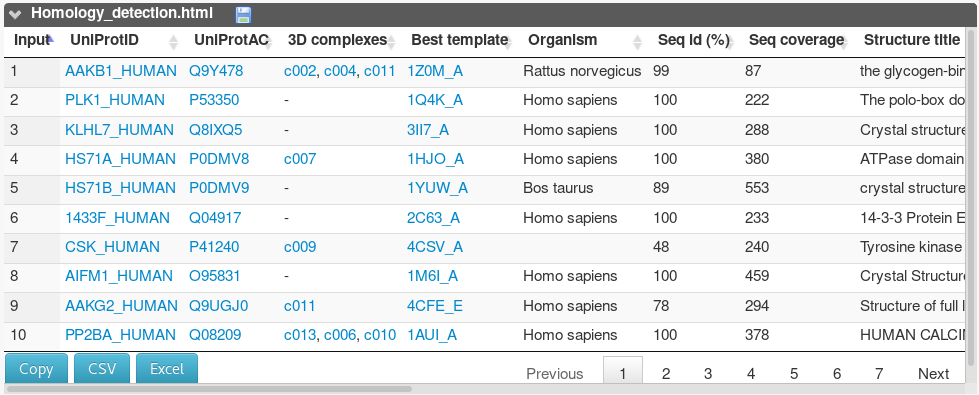
The homology_detection table summarizes the results of the homology search.
For each input sequence, it reports the hetero-complexes in which the protein was detected to participate in, and information about the best template identified by HHsearch (PDB identifier, organism, sequence identity, coverage). For instance, the AAKB1 (Q9Y478) is found to belong to 3 hetero-complexes (c002, c004 and c011).
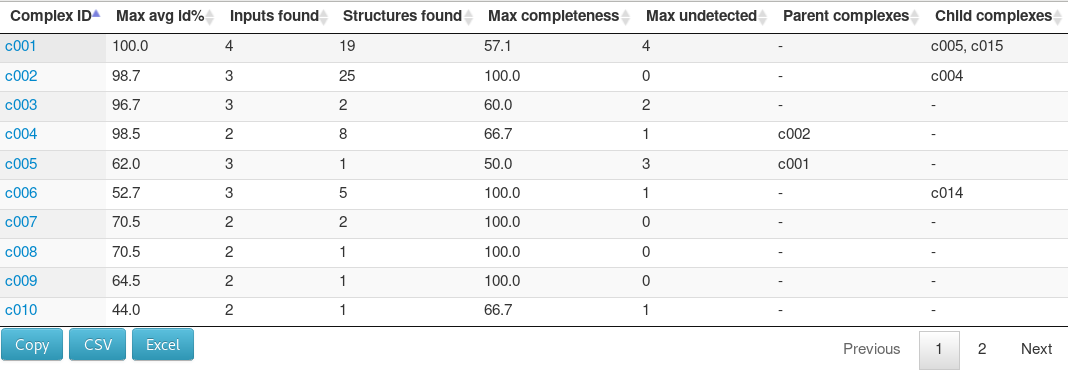
A second table summarizes the results of the search for protein hetero-complexes.
It summarizes the 3D complexes with experimental structures identified as involving the input data. Complexes are denoted as c001, etc.
The table columns describe, from left to right: the complex unique identifier, the maximal average sequence identity of chain with the corresponding protein of the input data over all equivalent template complexes of known structure identified, the number of input proteins mapped to the complex structure, the number of PDB structures corresponding to similar complexes, the maximum completeness of the input/template alignment, the number of chains of the template complex that do not have an identified equivalent in the input data, the parent and child complex identifiers for entries corresponding to smaller complexes.
For instance, for c001, one observes that 4 over 8 chains seem not to have an equivalent in the input data. One also sees that c002 (3 chains) seems to correspond to an assembly encompassing that of c004 (2 chains).
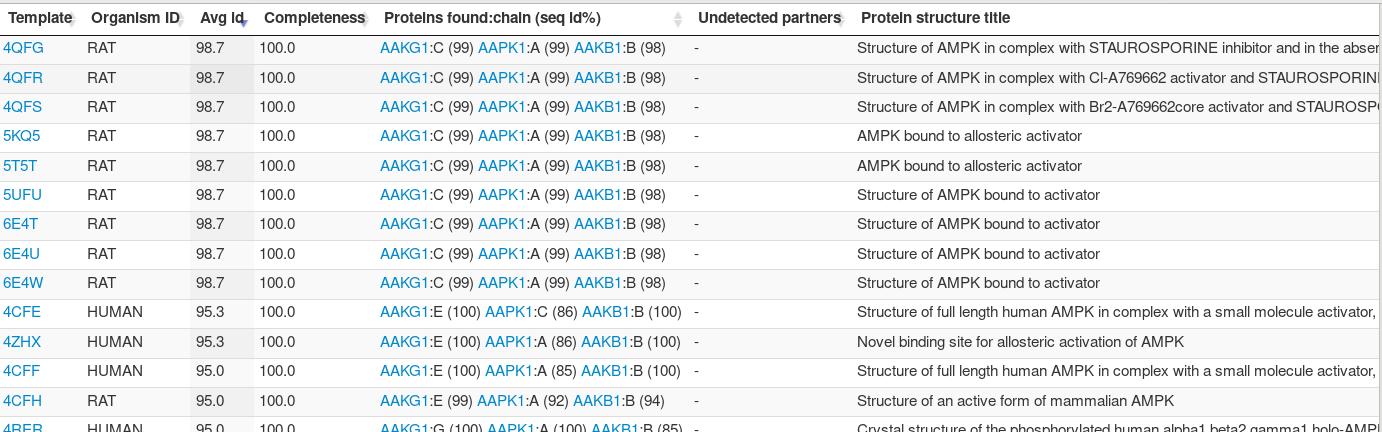
Clicking on the complex unique identifier gives access to an ancillary table describing the mapping between the complex structures and the input proteins. For instance, clicking on the complex c002, the table describes the input mapping to all chains of all 25 structures identified with the same assembly, belonging to different species. Interestingly, one sees that better sequence identity seems to occur for structures resolved for the RAT (98.7%), and not for H. Sapiens (95.3%). Looking in more detail, one observes that this difference comes in fact from AAPK1 (86%), as the human structure contains the AAPK2 paralog instead of AAPK1.
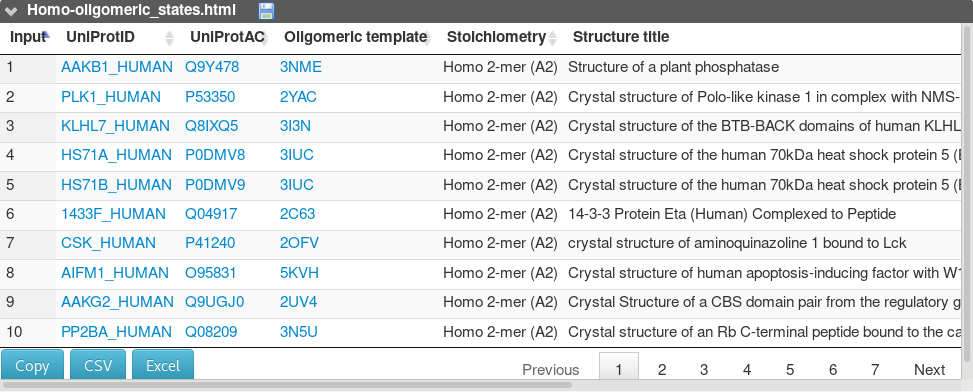
A third table summarizes the results of the homo-oligomeric state of each protein.
It reports for each input protein, the oligomeric state proposed in the biological unit of the template structure, as proposed in the PDB. Author's assignments are preferred to PISA prediction. For instance, a dimeric state is proposed for the PLK1_HUMAN (P53350), not detected as belonging to a hetero-complex (see above).